How Pregabalin Works: Mechanism, Effects and Duration
Introduction
Pregabalin is widely prescribed for nerve pain, anxiety disorders and certain types of seizures, but its unique action within the nervous system is what makes it so effective. Understanding how Pregabalin works helps explain why it offers relief for chronic conditions and why it must be taken under medical supervision. This guide covers its mechanism of action, onset, duration and the factors that influence how it behaves in the body.
How Pregabalin Works in the Body
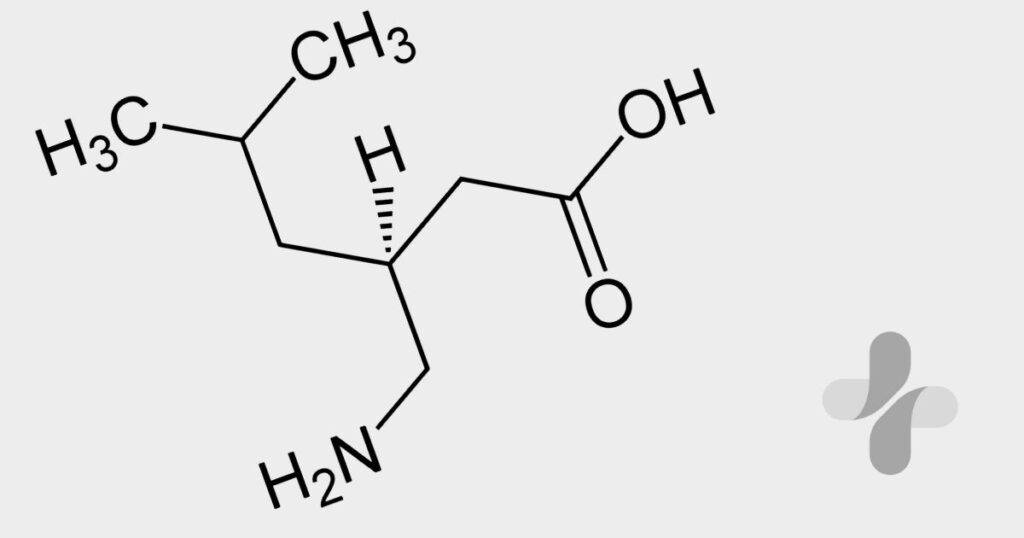
Pregabalin works by binding to voltage-gated calcium channels in the brain and spinal cord. These channels play a major role in transmitting pain signals and regulating the release of neurotransmitters involved in nerve communication. When Pregabalin attaches to these channels, it reduces the release of substances such as glutamate, norepinephrine and substance P—chemicals responsible for escalating nerve pain and anxiety. By limiting their activity, Pregabalin reduces abnormal electrical signals and calms overactive nerves.
Therapeutic Effects of Pregabalin
Because Pregabalin stabilises nerve activity, it provides several therapeutic benefits. For individuals with neuropathic pain, such as diabetic neuropathy or nerve damage from shingles, Pregabalin can significantly reduce burning, tingling or shooting pain. It also helps manage fibromyalgia symptoms by reducing widespread nerve sensitivity. In cases of generalised anxiety disorder, its calming effect on nerve signalling can lower excessive worry and tension. When used for epilepsy, Pregabalin acts as an add-on therapy to help prevent partial seizures by reducing abnormal electrical discharges in the brain.
Onset of Action
Pregabalin is absorbed quickly by the body, and many individuals begin feeling its effects within a few days of starting treatment. However, the full therapeutic benefits—especially for chronic nerve pain—may take two to four weeks to develop. The medication’s fast absorption rate makes dosing predictable and consistent, which is especially useful for long-term management of nerve-related conditions.
Duration and Half-Life of Pregabalin
Pregabalin has a relatively short half-life of around six hours, meaning it does not stay in the body as long as many other nerve pain medications. For this reason, it is typically taken two to three times daily, depending on the specific condition being treated. Despite its short half-life, its effects can accumulate with regular use, helping maintain stable symptom control over time. Extended-release versions, where available, are designed to offer steadier coverage throughout the day.
Why Pregabalin’s Mechanism Matters
Pregabalin’s targeted effect on calcium channels makes it especially useful for nerve-origin pain, which does not respond well to standard painkillers like ibuprofen or paracetamol. By working directly on nerve communication, it addresses the underlying cause of neuropathic pain rather than just masking symptoms. However, because it suppresses nerve activity, Pregabalin can also cause drowsiness, dizziness and coordination issues, which means users must be cautious when driving or performing tasks that require focus.
Factors That Influence Pregabalin’s Effects
Pregabalin’s effectiveness can vary based on several factors. Kidney function plays a key role, as the medication is processed almost entirely through the kidneys. Individuals with kidney issues may require significantly lower doses. Age can also influence how the body handles Pregabalin, with older adults sometimes experiencing stronger or longer-lasting effects. Taking Pregabalin with alcohol, opioids or other sedatives can amplify drowsiness and increase safety risks. These factors make careful dosing and medical supervision essential.
Importance of Using Pregabalin Safely
While Pregabalin can greatly improve symptoms of nerve pain and anxiety, safe use is crucial. The medication can cause dependence if taken for long periods or in higher-than-prescribed doses. Stopping Pregabalin suddenly may lead to withdrawal symptoms such as nausea, anxiety, headaches or insomnia, so it should always be tapered gradually under medical guidance. Understanding how the medication works helps users follow dosing correctly and avoid unnecessary complications.
Summary
Pregabalin works by calming overactive nerves through its action on calcium channels in the brain and spinal cord. This mechanism makes it highly effective for treating chronic nerve pain, anxiety disorders and partial seizures. Its predictable onset and short half-life support stable symptom relief when used correctly. However, because of its potential for side effects, dependence and interactions, Pregabalin must be taken responsibly and under professional supervision to ensure safe and effective treatment.